Introduction
A basic budgeting vocabulary chart serves as an essential tool for anyone looking to gain financial literacy and take control of their money. Budgeting is not just about numbers on a spreadsheet—it’s about understanding the terminology that drives financial decisions. Whether you’re managing household expenses, saving for retirement, or planning a vacation, knowing key budgeting terms is the foundation of successful money management.
Without a clear understanding of budgeting vocabulary, even the best budgeting tools or strategies can fall flat. Terms like gross income, fixed expenses, and emergency funds are more than jargon—they’re the building blocks of financial stability. This article will walk you through every essential term you need to know, offer practical examples, and include a downloadable basic budgeting vocabulary chart to keep these terms at your fingertips.
Table of Contents

2. Why a Basic Budgeting Vocabulary Chart is Essential
A basic budgeting vocabulary chart simplifies complex financial jargon, making it easier for individuals and families to understand how to manage their income and expenses. Here’s why it’s crucial:
- Empowers Financial Decisions: Knowing budgeting terms helps you make smarter choices.
- Improves Communication: Understand financial documents, bank statements, and investment opportunities.
- Prevents Financial Mistakes: Awareness of key terms helps you avoid pitfalls like overspending or taking on high-interest debt.
- Boosts Confidence: With knowledge comes confidence to discuss money matters and seek professional advice.
Imagine trying to assemble furniture without reading the instruction manual. Financial terms work the same way—they guide you through creating, adjusting, and sticking to a budget effectively.
3. Key Budgeting Terms Every Beginner Should Know
The basic budgeting vocabulary chart includes terms you’ll encounter regularly. Let’s break them down:
- Budget: A plan for managing income and expenses over a set period.
- Income: Money earned from various sources such as jobs, investments, or passive streams.
- Expenses: Money spent on needs, wants, and financial obligations.
- Debt: Money owed to lenders, including loans and credit card balances.
- Savings: Money set aside for future needs or emergencies.
- Deficit: When expenses exceed income.
- Surplus: When income exceeds expenses.
These fundamental terms are essential for building and maintaining financial stability.
4. Income-Related Terms in a Basic Budgeting Vocabulary Chart
Income is the foundation of any budget. The basic budgeting vocabulary chart highlights these key terms:
- Gross Income: Your total earnings before taxes and other deductions.
- Net Income: Your take-home pay after deductions.
- Passive Income: Money earned with minimal active involvement (e.g., rental income, dividends).
- Disposable Income: The money left after paying taxes and necessary expenses.
Example: If you earn $4,000 monthly and taxes/deductions take $1,000, your net income is $3,000. Understanding these distinctions helps you budget more effectively.
5. Expense-Related Terms in a Basic Budgeting Vocabulary Chart
Expenses play a critical role in budgeting. The basic budgeting vocabulary chart categorizes them into:
- Fixed Expenses: Costs that remain the same each month (e.g., rent, car payments).
- Variable Expenses: Costs that change from month to month (e.g., groceries, fuel).
- Discretionary Expenses: Non-essential spending (e.g., eating out, entertainment).
- Recurring Expenses: Payments made regularly, like subscriptions.
Knowing these categories helps allocate funds more strategically and prevents overspending.
6. Saving and Investment Terms in a Basic Budgeting Vocabulary Chart
A strong financial plan includes saving and investing. The basic budgeting vocabulary chart explains:
- Emergency Fund: Savings set aside specifically for unexpected expenses.
- Savings Account: A bank account designed for short-term or long-term savings.
- Compound Interest: Interest earned on both your initial investment and previously earned interest.
- Investment Portfolio: A collection of assets, including stocks, bonds, and mutual funds.
An emergency fund is often recommended to cover three to six months’ worth of living expenses.
7. Debt and Credit Terms in a Basic Budgeting Vocabulary Chart
Understanding debt terminology is crucial for avoiding financial traps. Common terms in the basic budgeting vocabulary chart include:
- Credit Score: A number indicating your creditworthiness.
- Interest Rate: The cost of borrowing money.
- Debt Consolidation: Combining multiple debts into one loan with a lower interest rate.
- Minimum Payment: The smallest amount you must pay on a loan or credit card each month.
These terms help you navigate credit cards, loans, and repayment plans responsibly.
8. Budgeting Techniques and Methods Explained
Popular budgeting techniques include:
- 50/30/20 Rule: Allocate income into needs (50%), wants (30%), and savings (20%).
- Zero-Based Budgeting: Every dollar is assigned a purpose.
- Envelope System: Allocate cash into envelopes for different spending categories.
- Pay Yourself First: Prioritize savings before spending on anything else.
Choose a method that aligns with your financial goals.
9. Tools to Implement a Basic Budgeting Vocabulary Chart
Budgeting tools and apps simplify tracking and managing finances. Popular tools include:
- Mint: Tracks spending and budgets automatically.
- YNAB (You Need A Budget): Focuses on giving every dollar a purpose.
- PocketGuard: Prevents overspending.
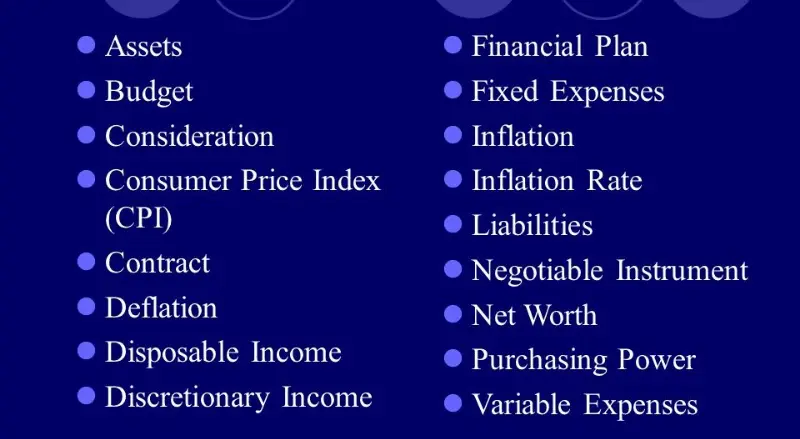
10. Real-Life Application of a Basic Budgeting Vocabulary Chart
Let’s take an example:
- Income: $4,500 (net income)
- Fixed Expenses: $1,800 (rent, car payment)
- Variable Expenses: $700 (groceries, fuel)
- Savings: $1,000
- Discretionary Spending: $1,000
By understanding these terms, you can make adjustments, save more, or reduce unnecessary expenses.
11. Budgeting Vocabulary Chart for Quick Reference
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Gross Income | Total earnings before deductions. |
| Net Income | Earnings after deductions. |
| Fixed Expense | Monthly recurring cost. |
| Variable Expense | Costs that fluctuate monthly. |
| Emergency Fund | Savings for unexpected events. |
12. Benefits of Mastering a Basic Budgeting Vocabulary Chart
- Greater financial confidence
- Better money management
- Improved savings habits
- Debt reduction
13. FAQs
Q1: Why is a budgeting vocabulary chart important?
A: It simplifies financial terms, making budgeting easier to understand.
Q2: What is the difference between gross and net income?
A: Gross income is pre-deduction earnings, while net income is post-deduction earnings.
14. Conclusion
A basic budgeting vocabulary chart is more than just a glossary—it’s your guide to smarter financial management. By understanding these key terms, you’ll gain clarity, confidence, and control over your money.
15. External Resources for Financial Education
For more in-depth financial education, visit: Investopedia
Explore More Tips and Insights!
Looking for more helpful articles like this one? Check out our latest posts here and stay updated with the best tips, tricks, and guides.

